Understanding Energy and Nutrition
Energy is the foundation of everything we do, from breathing and thinking to exercising and working. The food we eat serves as fuel for our bodies, providing the calories and nutrients necessary to power our cells, organs, and muscles. However, not all foods provide energy equally. Some foods offer quick bursts of energy followed by crashes, while others provide sustained, long-lasting fuel that keeps you alert and productive throughout the day. Understanding which foods give you the best energy is key to optimizing your diet for performance, productivity, and overall well-being.
The body derives energy primarily from three macronutrients: carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Carbohydrates are the body's preferred and most readily available source of energy, broken down into glucose that fuels cellular processes. Fats provide the most concentrated source of energy, with nine calories per gram compared to four calories per gram for carbohydrates and proteins. Proteins can also be used for energy but are primarily used for building and repairing tissues. The key to sustained energy lies in choosing foods that provide a balanced combination of these macronutrients, along with essential vitamins and minerals that support energy metabolism.
Complex Carbohydrates for Sustained Energy
Complex carbohydrates are among the best foods for providing sustained energy throughout the day. Unlike simple carbohydrates found in candy, soda, and white bread, which are quickly digested and cause rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar, complex carbohydrates are broken down slowly, providing a steady stream of glucose to the bloodstream. This results in more consistent energy levels without the peaks and valleys associated with simple sugars.
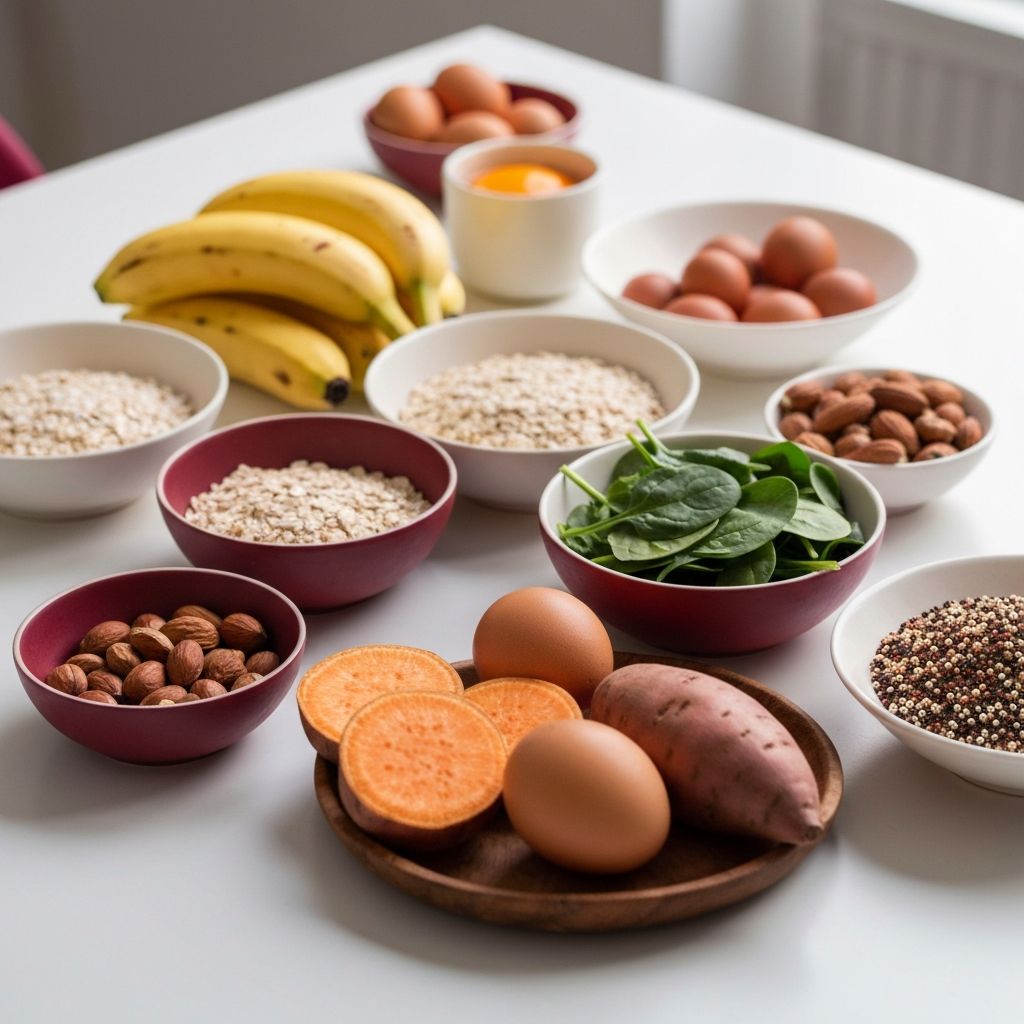
Oatmeal is one of the best complex carbohydrate sources for energy. A bowl of steel-cut or rolled oats provides a combination of complex carbohydrates, fiber, and a moderate amount of protein that can keep you fueled for hours. The beta-glucan fiber in oats slows digestion and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. Adding toppings like nuts, seeds, and berries can further enhance the nutritional profile and energy-sustaining properties of your oatmeal.
Brown rice, quinoa, sweet potatoes, and whole wheat bread are other excellent sources of complex carbohydrates. Brown rice provides sustained energy along with B vitamins that are essential for energy metabolism. Quinoa is unique among grains because it is a complete protein, containing all nine essential amino acids, making it an exceptionally well-rounded energy source. Sweet potatoes are rich in complex carbohydrates, fiber, and vitamin A, providing long-lasting energy along with important micronutrients.
Protein-Rich Foods for Lasting Power
Protein plays a crucial role in maintaining energy levels by providing a slow, steady source of fuel and by promoting satiety, which prevents the energy crashes associated with hunger. Foods rich in protein help stabilize blood sugar levels and provide the building blocks for neurotransmitters that regulate alertness and mood.
Eggs are one of the most nutrient-dense, energy-providing foods available. A single large egg contains about six grams of high-quality protein, along with healthy fats, B vitamins, and choline, a nutrient important for brain function and energy metabolism. The protein and fat in eggs provide sustained energy without causing blood sugar spikes, making them an ideal breakfast food for lasting morning energy.
Lean meats such as chicken breast, turkey, and fish are excellent sources of protein that provide sustained energy. Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines offer the additional benefit of omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to reduce inflammation and support brain function. Greek yogurt is another outstanding protein source, containing about 15 to 20 grams of protein per serving along with probiotics that support digestive health and nutrient absorption.
Plant-based protein sources like lentils, chickpeas, black beans, and edamame are excellent energy-boosting options for vegetarians and vegans. Legumes provide a powerful combination of protein, complex carbohydrates, and fiber that delivers sustained energy while supporting digestive health. A single cup of cooked lentils provides about 18 grams of protein and 40 grams of carbohydrates, making it one of the most energy-dense plant foods available.
Healthy Fats That Fuel Your Body
Healthy fats are an essential component of an energy-boosting diet. While fats are calorie-dense, they provide a concentrated and long-lasting source of energy that is particularly beneficial for endurance activities and sustained mental focus. The key is choosing unsaturated fats and omega-3 fatty acids while limiting saturated and trans fats.
Nuts and seeds are among the best sources of healthy, energy-boosting fats. Almonds, walnuts, cashews, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and pumpkin seeds all provide a combination of healthy fats, protein, and fiber that delivers sustained energy. A small handful of almonds, for example, provides about 160 calories of long-lasting energy along with vitamin E, magnesium, and manganese. Chia seeds are particularly noteworthy, as they can absorb up to 12 times their weight in water, helping to maintain hydration and prolong the release of energy from food.
Avocados are another excellent source of energy-boosting healthy fats. Rich in monounsaturated fatty acids, fiber, and potassium, avocados provide sustained energy and help maintain stable blood sugar levels. The combination of healthy fats and fiber in avocados slows digestion, providing a steady release of energy over several hours. Adding avocado to meals or snacks can help prevent the energy dips that often occur between meals.
Fruits and Vegetables That Energize
Fruits and vegetables are vital energy sources that provide natural sugars, fiber, vitamins, and minerals essential for energy production. Bananas are often called nature's energy bar, and for good reason. They are rich in natural sugars (glucose, fructose, and sucrose), potassium, vitamin B6, and fiber. The combination of quick-acting sugars and fiber provides both immediate and sustained energy, making bananas an ideal pre-workout snack or midday pick-me-up.
Berries, including blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries, are excellent energy-boosting fruits that provide natural sugars along with antioxidants, vitamins, and fiber. The antioxidants in berries help combat oxidative stress, which can contribute to fatigue. Oranges and other citrus fruits provide vitamin C and natural sugars for a quick energy boost, while apples offer a combination of fiber and natural sugars for sustained energy.
Dark leafy greens like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are packed with iron, magnesium, and folate, all of which are essential for energy production at the cellular level. Iron deficiency is one of the most common nutritional causes of fatigue, particularly in women, and incorporating iron-rich greens into your diet can help maintain optimal energy levels. Beets are another energy-boosting vegetable, containing natural nitrates that improve blood flow and oxygen delivery to muscles, enhancing both physical and mental energy.
Superfoods and Natural Energy Boosters
Several foods and beverages are particularly noted for their energy-boosting properties. Green tea provides a moderate amount of caffeine along with L-theanine, an amino acid that promotes calm alertness without the jitters associated with coffee. The combination of caffeine and L-theanine in green tea has been shown to improve focus, concentration, and sustained energy.
Dark chocolate, particularly varieties with 70 percent or higher cacao content, contains caffeine, theobromine, and antioxidants that can boost energy and mood. The moderate amount of natural sugars in dark chocolate provides quick energy, while the fats and fiber slow digestion for a more sustained effect. However, dark chocolate should be consumed in moderation due to its calorie density.
Water deserves special mention as the most fundamental energy requirement. Even mild dehydration can cause significant fatigue, reduced concentration, and decreased physical performance. Drinking adequate water throughout the day is one of the simplest and most effective ways to maintain energy levels. Aim for at least eight glasses of water daily, with more during exercise or in hot weather.
Conclusion
The best foods for energy are those that provide a balanced combination of complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, healthy fats, and essential vitamins and minerals. Foods like oatmeal, eggs, nuts, bananas, leafy greens, and fatty fish offer sustained energy without the crashes associated with processed and sugary foods. By building your diet around these nutrient-dense whole foods and staying well-hydrated, you can maintain consistent energy levels throughout the day and support your overall health and well-being.